Options Spreads 101: A Beginner’s Guide

Welcome to “Options Spreads 101: A Beginner’s Guide”! This guide will teach you everything you need about using options spreads as a trading strategy. Options spreads involve buying and selling multiple options simultaneously and can be a powerful way to manage risk and potentially generate profits.
This guide will cover the different options spreads, including call credit spreads, call debit spreads, put credit spreads, and put debit spreads. You will learn how to create each type of spread and when and why you might use them. We will also delve into advanced topics such as adjustments and choosing the right options for your spread.
By the end of this guide, you will thoroughly understand options spreads and be well-equipped to start using them in your trading. So let’s get started on your journey to mastering options spreads!

Table of Contents
I. Introduction
- Definition of Options Spreads
- Benefits and Risks of Using Options Spreads
II. Call Credit Spreads
- How to Create a Call Credit Spread
- When to Use a Call Credit Spread
- Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
III. Call Debit Spreads
- How to Create a Call Debit Spread
- When to Use a Call Debit Spread
- Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
IV. Put Credit Spreads
- How to Create a Put Credit Spread
- When to Use a Put Credit Spread
- Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
V. Put Debit Spreads
- How to Create a Put Debit Spread
- When to Use a Put Debit Spread
- Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
VI. Advanced Topics
- Adjustments to Options Spreads
- Choosing the Right Options for the Spread
- Factors to Consider When Using Options Spreads
VII. Conclusion
Definition of Options Spreads
An options spread is a strategy that simultaneously buys and sells options of the same class, such as call options or put options, with different strike prices and expiration dates. Options spreads can be used to reduce risk, generate income, or bet on the direction of the underlying security. There are various options spreads, including debit, credit, calendar, and diagonal spreads. Options spreads can be used in bullish and bearish market environments and are popular among options traders.
Benefits and Risks of Using Options Spreads
One of the main benefits of using option spreads is potentially reducing risk. By spreading the risk across multiple options, you can limit your potential loss if the trade does not go as planned. Options spreads can also be used to generate income, as you may be able to collect premiums from the options you sell.
However, there are also risks associated with using options spreads. One risk is that the spread may not perform as expected, resulting in a loss. There is also the risk of time decay, as options lose value as they get closer to expiration. It is essential to consider the potential risks and rewards of using options spreads before implementing them in your trading strategy.
Call Credit Spreads
A call credit spread, also known as a bull call spread, is an options spread strategy involving buying and selling one call option with a higher strike price. A call credit spread aims to profit from a moderate rise in the underlying security price. The trader receives a net credit when entering the position, as the premium received from the short call option is greater than the premium paid for the long call option.
If the underlying security price remains below the strike price of the long call option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will keep the net credit as profit. If the price of the underlying security increases above the strike price of the long call option, the spread may incur a loss, but the loss will be limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received.

How to Create a Call Credit Spread
To create a call credit spread, you will need to follow these steps:
- Select the underlying security and expiration date for the options.
- Choose the strike price for the long call option. This should be a price at which you believe the underlying security will not rise significantly.
- Choose a higher strike price for the short call option. This will be the option that you sell.
- Enter an order to buy the long call option and sell the short call option. Make sure to specify that you want to create a spread by choosing “spread” or “vertical spread” in the order type.
- Confirm the details of your spread, including the net credit you will receive and the maximum potential profit and loss.
- Submit the order and wait for it to be filled.
It is important to note that you will need a margin account to create a call credit spread, as you will be selling the short-call option. You will also need to have enough funds in your account to cover the cost of the long call option and any potential losses.
When to Use a Call Credit Spread
A call credit spread may be a good strategy to use in the following situations:
- When you expect the underlying security price to rise moderately: By selling a call option with a higher strike price, you are betting that the underlying security will not rise significantly above that price. You can keep the net credit received as profit if your prediction is correct.
- When you want to generate income: Because you receive a net credit when entering a call credit spread, you can potentially generate income from the trade even if the underlying security does not move in price.
- When you want to limit your potential loss: If the underlying security price rises above the strike price of the long call option, your loss will be limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received. This can be a good way to manage risk if you are unsure of the market’s direction.
It is important to note that a call credit spread may not be suitable for all market environments. Before using this strategy, you should consider your own goals and risk tolerance.
Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
There are several potential profit and loss scenarios for a call credit spread. Here are a few examples:
- If the underlying security price remains below the strike price of the long call option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will keep the net credit received as profit. For example, if a trader enters a call credit spread with a net credit of $50, and the spread expires worthless, their profit will be $50.
- If the price of the underlying security increases above the strike price of the long call option but remains below the strike price of the short call option at expiration, the trader will incur a loss. The loss will be the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received. For example, if the spread has a net credit of $50 and the difference between the strike prices is $100, and the underlying security price increases to $80 at expiration, the trader’s loss will be $50 (100 – 50 – 80).
- If the price of the underlying security increases above the strike price of the short call option at expiration, the trader will incur a loss equal to the difference between the strike prices. In this case, the net credit received will not offset the loss.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of potential profit and loss scenarios for a call credit spread. The actual outcome will depend on the spread’s specific details and the underlying security movement.
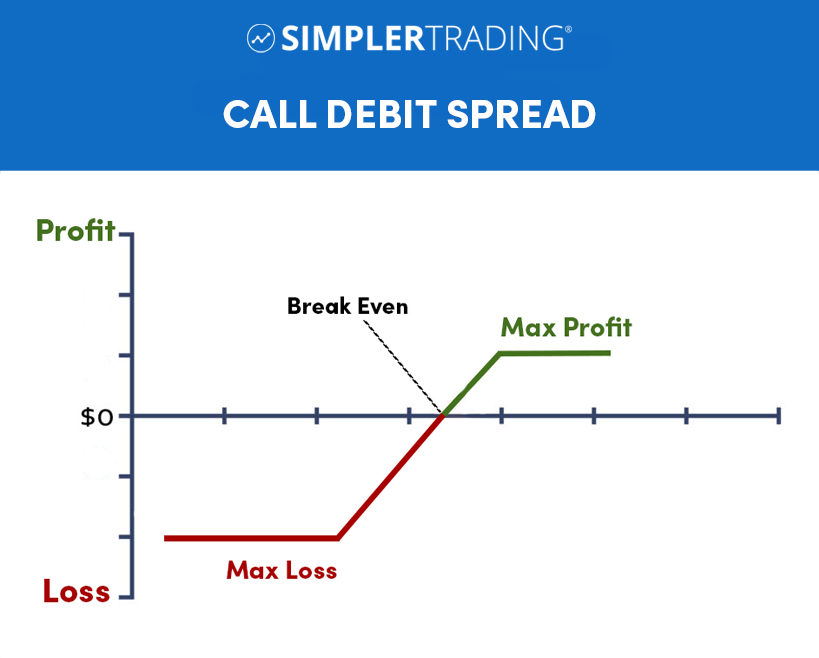
Call Debit Spreads
A call debit spread, also known as a bull call spread, is an options spread strategy involving buying and selling one call option with a lower strike price. The goal of a call debit spread is to profit from a moderate rise in the underlying security price. The trader pays a net debit when entering the position, as the premium paid for the long call option is greater than the premium received from the short call option.
If the underlying security price remains below the strike price of the long call option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will lose the net debit paid. If the price of the underlying security increases above the strike price of the long call option, the spread may generate a profit, with the potential profit being limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net debit paid.
How to Create a Call Debit Spread
To create a call debit spread, you will need to follow these steps:
- Select the underlying security and expiration date for the options.
- Choose the strike price for the long call option. This should be a price at which you believe the underlying security will rise moderately.
- Choose a lower strike price for the short-call option. This will be the option that you sell.
- Enter an order to buy the long call option and sell the short call option. Make sure to specify that you want to create a spread by choosing “spread” or “vertical spread” in the order type.
- Confirm the details of your spread, including the net debit you will pay and the maximum potential profit and loss.
- Submit the order and wait for it to be filled.
It is important to note that you will need a margin account to create a call debit spread, as you will be selling the short-call option. You will also need to have enough funds in your account to cover the cost of the long call option and any potential losses.
When to Use a Call Debit Spread
A call debit spread may be a good strategy to use in the following situations:
- When you expect the price of the underlying security to rise moderately: By buying a call option with a lower strike price and selling a call option with a higher strike price, you are betting that the underlying security will rise but not significantly exceed the strike price of the long call option. If your prediction is correct, you may be able to generate a profit from the trade.
- When you have a bullish outlook on the market: A call debit spread can be a way to bet on an upward move in the underlying security price.
- When you want to limit your potential loss: If the underlying security price does not rise above the strike price of the long call option, your loss will be limited to the net debit paid. This can be a good way to manage risk if you are unsure of the market’s direction.
It is important to note that a call debit spread may not be suitable for all market environments. Before using this strategy, consider your goals and risk tolerance.
Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
There are several potential profit and loss scenarios for a call debit spread. Here are a few examples:
- If the underlying security price remains below the strike price of the long call option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will lose the net debit paid. For example, if a trader enters a call debit spread with a net debit of $50, and the spread expires worthless, their loss will be $50.
- Suppose the price of the underlying security increases above the strike price of the long call option but remains below the strike price of the short call option at expiration. In that case, the trader will generate a profit. The profit will be the difference between the strike prices minus the net debit paid. For example, suppose the spread has a net debit of $50. In that case, the difference between the strike prices is $100, and the underlying security price increases to $80 at expiration, the trader’s profit will be $50 (80 – 50 – 100).
- If the price of the underlying security increases above the strike price of the short call option at expiration, the trader will incur a loss equal to the difference between the strike prices. In this case, the net debit paid will not offset the loss.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of potential profit and loss scenarios for a call debit spread. The actual outcome will depend on the spread’s specific details and the underlying security’s movement.
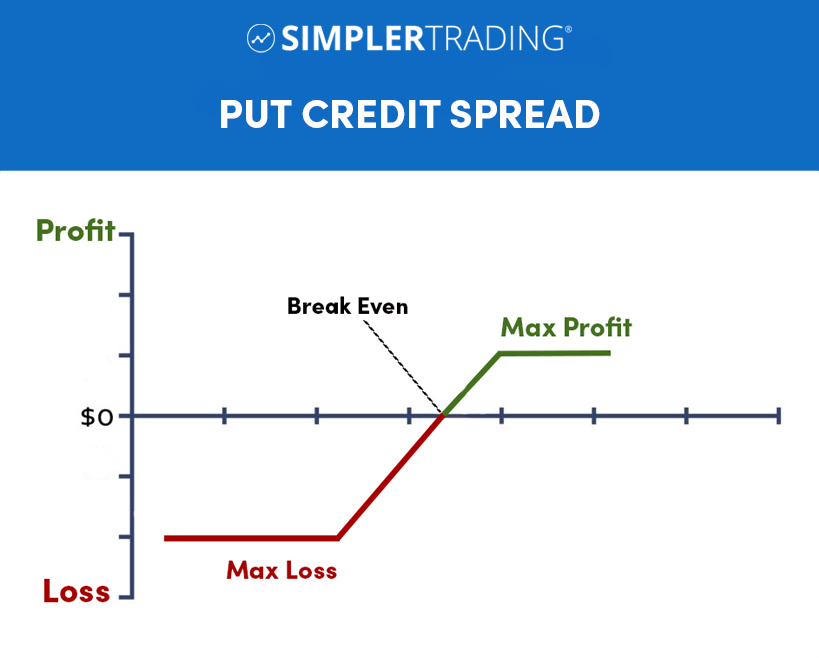
Put Credit Spreads
A put credit spread, also known as a bear put spread, is an options spread strategy involving buying and selling one put option with a lower strike price. A put credit spread aims to profit from a moderate decline in the underlying security price. The trader receives a net credit when entering the position, as the premium received from the short put option is greater than the premium paid for the long put option.
If the underlying security price remains above the strike price of the long put option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will keep the net credit received as profit. If the underlying security price decreases below the strike price of the long put option, the spread may incur a loss, but the loss will be limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received.
How to Create a Put Credit Spread
To create a put credit spread, you will need to follow these steps:
- Select the underlying security and expiration date for the options.
- Choose the strike price for the long put option. This should be a price at which you believe the underlying security will not decline significantly.
- Choose a lower strike price for the short put option. This will be the option that you sell.
- Enter an order to buy the long put option and sell the short put option. Make sure to specify that you want to create a spread by choosing “spread” or “vertical spread” in the order type.
- Confirm the details of your spread, including the net credit you will receive and the maximum potential profit and loss.
- Submit the order and wait for it to be filled.
It is important to note that you will need a margin account to create a put credit spread, as you will be selling the short put option. You will also need to have enough funds in your account to cover the cost of the long put option and any potential losses.
When to Use a Put Credit Spread
A put credit spread may be a good strategy to use in the following situations:
- When you expect the underlying security price to decline moderately: By selling a put option with a lower strike price, you are betting that the underlying security will not decline significantly below that price. You can keep the net credit received as profit if your prediction is correct.
- When you want to generate income: Because you receive a net credit when entering a put credit spread, you can potentially generate income from the trade even if the underlying security does not move in price.
- When you want to limit your potential loss: If the underlying security price declines below the strike price of the long put option, your loss will be limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received. This can be a good way to manage risk if you are unsure of the market’s direction.
It is important to note that a put credit spread may not be suitable for all market environments. Before using this strategy, consider your goals and risk tolerance.

Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
There are several potential profit and loss scenarios for a put credit spread. Here are a few examples:
- If the underlying security price remains above the strike price of the long put option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will keep the net credit received as profit. For example, if a trader enters a put credit spread with a net credit of $50, and the spread expires worthless, their profit will be $50.
- If the underlying security price decreases below the strike price of the long put option but remains above the strike price of the short put option at expiration, the trader will incur a loss. The loss will be the difference between the strike prices minus the net credit received. For example, if the spread has a net credit of $50 and the difference between the strike prices is $100, and the underlying security price decreases to $80 at expiration, the trader’s loss will be $50 (100 – 50 – 80).
- Suppose the underlying security price decreases below the strike price of the short put option at expiration. In that case, the trader will incur a loss equal to the difference between the strike prices. In this case, the net credit received will not offset the loss.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of potential profit and loss scenarios for a put credit spread. The actual outcome will depend on the spread’s specific details and the underlying security’s movement. It is also important to note that these scenarios are for a put credit spread. The potential profit and loss scenarios for other types of options spreads, such as call credit spreads and debit spreads, may differ.
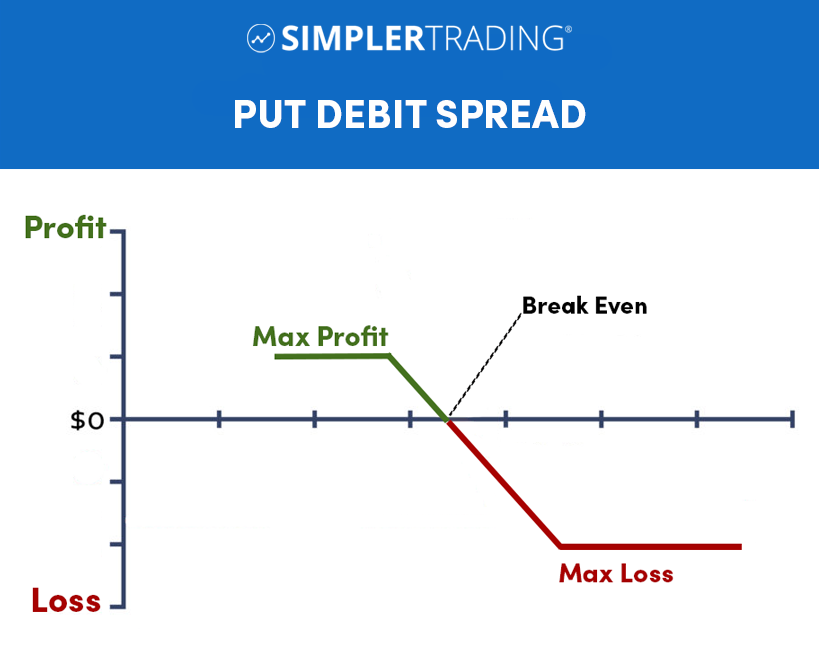
Put Debit Spreads
A put debit spread, also known as a bear put spread, is an options spread strategy involving buying and selling one put option with a higher strike price. The goal of a put debit spread is to profit from a moderate decline in the underlying security price. The trader pays a net debit when entering the position, as the premium paid for the long put option is greater than the premium received from the short put option.
If the underlying security price remains above the strike price of the long put option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will lose the net debit paid. Suppose the underlying security price decreases below the strike price of the long put option. In that case, the spread may generate a profit, with the potential profit being limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the net debit paid.
How to Create a Put Debit Spread
To create a put debit spread, you will need to follow these steps:
- Select the underlying security and expiration date for the options.
- Choose the strike price for the long put option. This should be a price at which you believe the underlying security will decline moderately.
- Choose a higher strike price for the short put option. This will be the option that you sell.
- Enter an order to buy the long put option and sell the short put option. Make sure to specify that you want to create a spread by choosing “spread” or “vertical spread” in the order type.
- Confirm the details of your spread, including the net debit you will pay and the maximum potential profit and loss.
- Submit the order and wait for it to be filled.
It is important to note that you will need a margin account to create a put debit spread, as you will be selling the short put option. You will also need to have enough funds in your account to cover the cost of the long put option and any potential losses.
When to Use a Put Debit Spread
A put debit spread may be a good strategy to use in the following situations:
- When you expect the price of the underlying security to decline moderately: By buying a put option with a lower strike price and selling a put option with a higher strike price, you are betting that the underlying security will decline but not significantly fall below the strike price of the long put option. If your prediction is correct, you may be able to generate a profit from the trade.
- When you have a bearish outlook on the market: A put debit spread can be a way to bet on a downward move in the underlying security price.
- When you want to limit your potential loss: If the underlying security price does not decline below the strike price of the long put option, your loss will be limited to the net debit paid. This can be a good way to manage risk if you are unsure of the market’s direction.
It is important to note that a put debit spread may not be suitable for all market environments. Before using this strategy, you should consider your own goals and risk tolerance.
Potential Profit and Loss Scenarios
There are several potential profit and loss scenarios for a put debit spread. Here are a few examples:
- If the underlying security price remains above the strike price of the long put option at expiration, the spread will expire worthless, and the trader will lose the net debit paid. For example, if a trader enters a put debit spread with a net debit of $50, and the spread expires worthless, their loss will be $50.
- Suppose the underlying security price decreases below the strike price of the long put option but remains above the strike price of the short put option at expiration. In that case, the trader will generate a profit. The profit will be the difference between the strike prices minus the net debit paid. For example, suppose the spread has a net debit of $50. In that case, the difference between the strike prices is $100, and the underlying security price decreases to $80 at expiration, the trader’s profit will be $50 (100 – 50 – 80).
- Suppose the underlying security price decreases below the strike price of the short put option at expiration. In that case, the trader will incur a loss equal to the difference between the strike prices. In this case, the net debit paid will not offset the loss.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of potential profit and loss scenarios for a put debit spread. The actual outcome will depend on the spread’s specific details and the underlying security movement.
Advanced Topics
Adjustments to Options Spreads
There may be times when a trader wants to adjust their options spread position to manage risk or take advantage of changes in market conditions. Here are a few common adjustments that traders make to options spreads:
- Rolling the spread to a different expiration date: If the trader believes that the underlying security will not move significantly in price before the current options expire, they may choose to roll the spread to a later expiration date. This can be a way to extend the trade and potentially generate additional income from the spread.
- Adjusting the strike prices: If the trader believes that the underlying security is likely to move significantly in price, they may choose to adjust the strike prices of the options in the spread. This could involve closing out one leg of the spread and replacing it with a new option at a different strike price.
- Adding or closing out the legs of the spread: In some cases, traders may want to add or close out the legs of the spread to adjust the risk/reward profile of the trade. For example, a trader may add a long call option to a call credit spread to reduce the potential loss of the trade.
Choosing the Right Options for the Spread
When choosing the options for an options spread, traders should consider the following factors:
- Underlying security: The underlying security will determine the price movements of the options in the spread. Traders should choose an underlying security that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Expiration date: The expiration date will determine how long the spread will be in place. Traders should choose an expiration date that gives the underlying security enough time to move in the desired direction but not so long that the options will be affected by significant changes in market conditions.
- Strike prices: The strike prices of the options in the spread will determine the potential profit and loss of the trade. Traders should choose strike prices that align with their expectations for the price movement of the underlying security.
- Option premiums: The option premiums, or the prices of the options, will affect the net cost or credit of the spread. Traders should consider the option premiums in relation to the potential profit and loss of the spread.
- Implied volatility: Implied volatility is a measure of the expected price movement of the underlying security. Options with higher implied volatility will generally have higher premiums, which can affect the net cost or credit of the spread. Traders should consider the level of implied volatility when choosing options for the spread.
Factors to Consider When Using Options Spreads
There are several factors that traders should consider when using options spreads. Here are a few examples:
- Market conditions: The market conditions at the time the spread is entered can affect the potential profit and loss of the trade. Traders should consider factors such as the market’s direction, volatility, and the economic and political environment when choosing options spreads.
- Risk tolerance: Options spreads involve a certain level of risk, and traders should choose strategies that align with their risk tolerance. For example, a trader with a low-risk tolerance may prefer strategies with a limited potential loss, such as credit spreads. In contrast, a trader with a high-risk tolerance may be more willing to take on larger potential losses in exchange for the possibility of higher returns.
- Investment goals: Options spreads can be used for a variety of investment goals, such as generating income, hedging a portfolio, or speculating on the direction of the market. Traders should choose strategies that align with their investment goals.
- Tax implications: Options spreads can have different tax implications depending on the specific details of the trade. Traders should know how their spreads will be taxed and plan accordingly.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, options spreads can be a powerful tool for traders looking to manage risk, generate income, or speculate on the market’s direction. By combining the buying and selling of options, traders can create customized positions that align with their investment goals and risk tolerance. However, it is essential to consider the factors that can affect an options spread’s potential profit and loss, including market conditions, risk tolerance, investment goals, and trading costs. If you want to learn more about options spreads and how to use them effectively, check out the Simpler Trading Options Trading Room. In this community of professional traders, you can learn strategies and techniques for successful options trading and get real-time support and guidance. Don’t miss this opportunity to take your options trading to the next level!

Recent Commentary & News

John Carter’s Favorite Options Trading Strategies
Feb 5, 2024

What Are Stock Options
Simpler Trading Team
Aug 14, 2023

Mastering Options Trading: The Ultimate Guide to Options Basics
Aug 5, 2023
Resources
Support
8911 North Capital of Texas Hwy
Suite 4200 #1005
Austin, TX 78759
The information contained on this website is solely for educational purposes, and does not constitute investment advice. The risk of trading in securities markets can be substantial. You must review and agree to our Disclaimers and Terms and Conditions before using this site.
U.S. Government Required Disclaimer – Commodity Futures Trading Commission. Futures and options trading has large potential rewards, but also large potential risk. You must be aware of the risks and be willing to accept them in order to invest in the futures and options markets. Don’t trade with money you can’t afford to lose. This website is neither a solicitation nor an offer to Buy/Sell futures or options. No representation is being made that any account will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those discussed on this website. The past performance of any trading system or methodology is not necessarily indicative of future results.
Individual results may vary, and testimonials are not claimed to represent typical results. All testimonials are by real people, and may not reflect the typical purchaser’s experience, and are not intended to represent or guarantee that anyone will achieve the same or similar results.
Simpler Trading’s Traders and employees will NEVER manage or offer to manage a customer or individual’s options, stocks, currencies, futures, or any financial markets or securities account. If someone claiming to represent or be associated with Simpler Trading solicits you for money or offers to manage your trading account, do not provide any personal information and contact us immediately.
CFTC RULE 4.41 – HYPOTHETICAL OR SIMULATED PERFORMANCE RESULTS HAVE CERTAIN LIMITATIONS. UNLIKE AN ACTUAL PERFORMANCE RECORD, SIMULATED RESULTS DO NOT REPRESENT ACTUAL TRADING. ALSO, SINCE THE TRADES HAVE NOT BEEN EXECUTED, THE RESULTS MAY HAVE UNDER-OR-OVER COMPENSATED FOR THE IMPACT, IF ANY, OF CERTAIN MARKET FACTORS, SUCH AS LACK OF LIQUIDITY, SIMULATED TRADING PROGRAMS IN GENERAL ARE ALSO SUBJECT TO THE FACT THAT THEY ARE DESIGNED WITH THE BENEFIT OF HINDSIGHT. NO REPRESENTATION IS BEING MADE THAT ANY ACCOUNT WILL OR IS LIKELY TO ACHIEVE PROFIT OR LOSSES SIMILAR TO THOSE SHOWN.
© 2024 Simpler Trading ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Reproduction without Permission Prohibited






![]()

